Polycarbonate Cladding Panels A Comprehensive Guide
Polycarbonate cladding panels offer a compelling blend of durability, aesthetics, and versatility. These panels, known for their impact resistance and lightweight nature, are transforming the landscape of architectural and industrial design. From sleek modern facades to robust industrial structures, polycarbonate’s unique properties are driving innovation across various sectors. This guide will explore the diverse applications, installation methods, and long-term benefits of choosing polycarbonate cladding.
We’ll delve into the specifics of different polycarbonate types – solid, multiwall, and corrugated – examining their strengths and weaknesses in different applications. We’ll also compare polycarbonate to other common cladding materials like aluminum and PVC, highlighting where polycarbonate excels and where other materials might be a better fit. Finally, we’ll discuss the environmental impact and cost-effectiveness of polycarbonate cladding, helping you make an informed decision for your next project.
Polycarbonate Cladding Panel Properties

Source: pinimg.com
Polycarbonate cladding panels are a popular choice for a variety of applications due to their unique combination of strength, lightness, and durability. Understanding their properties is crucial for selecting the right panel for a specific project. This section will delve into the key characteristics of these panels, comparing them to other common cladding materials and exploring their different types and lifespans.
Polycarbonate panels boast impressive physical properties. They are significantly stronger than many other cladding materials, offering excellent impact resistance and the ability to withstand harsh weather conditions. Their lightweight nature simplifies installation and reduces structural demands. Furthermore, they possess a degree of flexibility, allowing them to conform to curved surfaces, which opens up design possibilities. However, their flexibility also means they can be more susceptible to sagging than rigid materials like aluminum if not properly supported.
Polycarbonate Cladding Panel Comparison
To better understand the advantages of polycarbonate, let’s compare it to some common alternatives. The following table highlights key differences in strength, weight, and cost.
| Property | Polycarbonate | Aluminum | PVC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Impact Resistance | High | Moderate | Low |
| Weight | Light | Moderate | Light |
| Flexibility | Moderate | Low | Moderate |
| Cost | Moderate | High | Low |
Note that cost can vary significantly depending on the specific product and its thickness.
Types of Polycarbonate Cladding Panels
Polycarbonate cladding panels come in various forms, each suited to different applications and aesthetic preferences. Choosing the correct type is vital for achieving the desired outcome and ensuring longevity.
- Solid Polycarbonate Sheets: These offer excellent impact resistance and clarity, making them ideal for applications where transparency is desired, such as skylights or canopies.
- Multiwall Polycarbonate Sheets: These consist of multiple layers separated by air spaces, providing superior insulation and reduced weight compared to solid sheets. They are often used in roofing and wall cladding applications where thermal performance is important.
- Corrugated Polycarbonate Sheets: These sheets have a corrugated profile, providing structural rigidity and allowing for water runoff. They are frequently used in roofing and industrial applications.
UV Resistance and Lifespan
The longevity of polycarbonate cladding panels is heavily influenced by their UV resistance and exposure to various weather conditions. High-quality panels are typically treated with a UV-resistant coating to protect against degradation from sunlight. This coating significantly extends the lifespan of the panels, preventing yellowing and embrittlement. However, even with UV protection, extreme weather conditions such as prolonged exposure to intense sunlight, hailstorms, or extreme temperature fluctuations can impact the lifespan. Proper installation and maintenance are also crucial factors.
For instance, a well-maintained polycarbonate roof in a moderate climate with adequate UV protection might last for 20 years or more. In contrast, a poorly installed panel in a harsh desert environment might show significant degradation within a much shorter timeframe. Regular cleaning and inspection can help identify and address potential issues early, prolonging the lifespan of the panels.
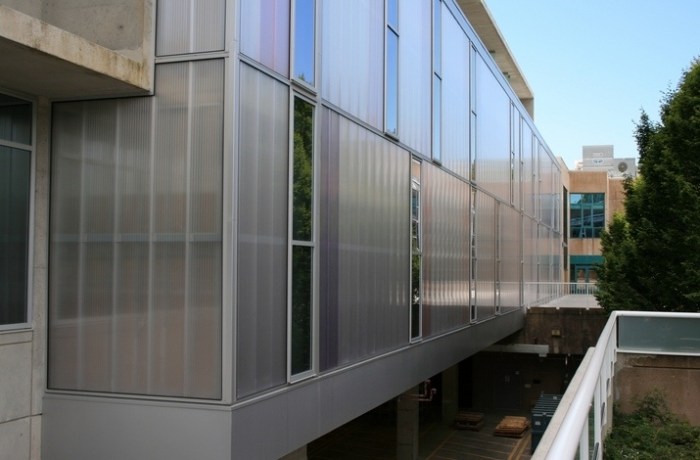
Applications of Polycarbonate Cladding Panels

Source: adsttc.com
Polycarbonate cladding panels, with their unique blend of strength, lightness, and optical clarity, find extensive use across a variety of architectural and industrial settings. Their versatility allows for creative design solutions while providing significant practical benefits, including durability and energy efficiency. Let’s explore some key application areas.
Architectural Applications of Polycarbonate Cladding
Polycarbonate’s lightweight yet robust nature makes it ideal for various architectural projects. Its ability to transmit light while offering protection from the elements is a significant advantage.
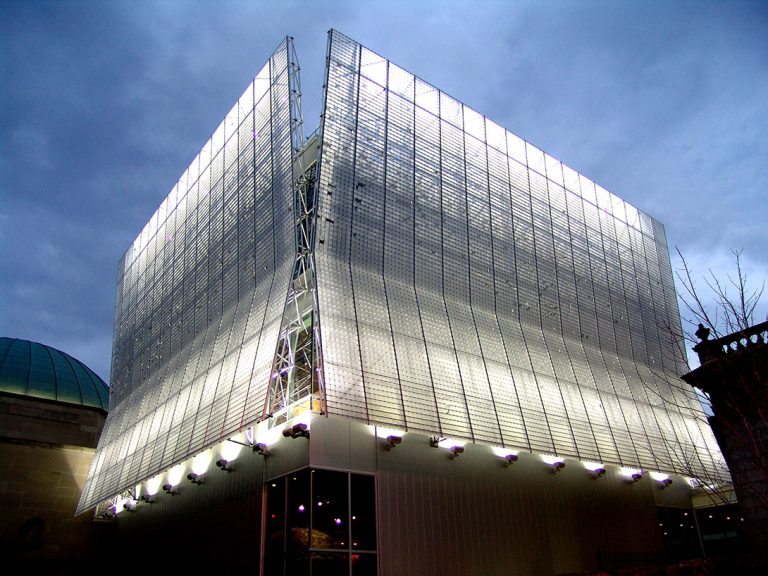
Facades: Imagine a modern office building with a sleek, curved facade crafted from polycarbonate panels. The panels allow ample natural light to penetrate the interior, reducing the need for artificial lighting and lowering energy costs. Simultaneously, the panels offer protection from harsh weather conditions, ensuring a comfortable and energy-efficient workspace. The inherent translucency of the panels can also be creatively exploited to create visually stunning and dynamic building exteriors.
Canopies: Consider a shopping mall entrance protected by a large, aesthetically pleasing canopy made of polycarbonate. This canopy shields shoppers from rain and sun, enhancing their shopping experience while adding a touch of modern elegance to the building’s design. The lightweight nature of the material also simplifies installation and reduces structural support requirements.
Roofing: Polycarbonate roofing panels are perfect for creating naturally lit atriums or skylights in commercial buildings or residential homes. The panels effectively diffuse sunlight, minimizing glare and providing even illumination while maintaining excellent weather resistance. This leads to a brighter, more pleasant interior space, reducing the reliance on artificial lighting and enhancing the overall ambiance.
Industrial Applications of Polycarbonate Cladding
The robust nature and resistance to impact and UV degradation make polycarbonate cladding panels a popular choice in industrial settings.
| Application | Benefits | Example | Further Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sound Barriers | High impact resistance, sound-dampening properties | Highway noise barriers | Reduces noise pollution effectively, requires minimal maintenance. |
| Greenhouses | High light transmission, UV protection, impact resistance | Agricultural greenhouses | Optimizes plant growth by maximizing light penetration while protecting plants from harsh weather. |
| Skylights | Lightweight, high light transmission, impact resistance | Factory skylights | Provides natural light to improve worker productivity and reduce energy consumption. Easy to install and maintain. |
| Machine Guards | Impact resistance, transparency for visibility | Industrial machinery enclosures | Protects workers from moving parts while allowing clear visibility of the machinery operation. |
Commercial Applications of Polycarbonate Cladding
Polycarbonate cladding offers both aesthetic and functional advantages in commercial settings.
In retail spaces, polycarbonate panels can be used to create eye-catching displays and visually appealing facades that attract customers. The panels’ ability to transmit light creates a bright and inviting atmosphere within the store, enhancing the shopping experience. In office buildings, polycarbonate can be used for interior partitions, allowing natural light to filter through while maintaining privacy. This creates a more open and airy workspace, improving employee morale and productivity. The use of polycarbonate can also contribute to a building’s LEED certification by reducing energy consumption.
Installation and Maintenance of Polycarbonate Cladding Panels

Source: danpal.com
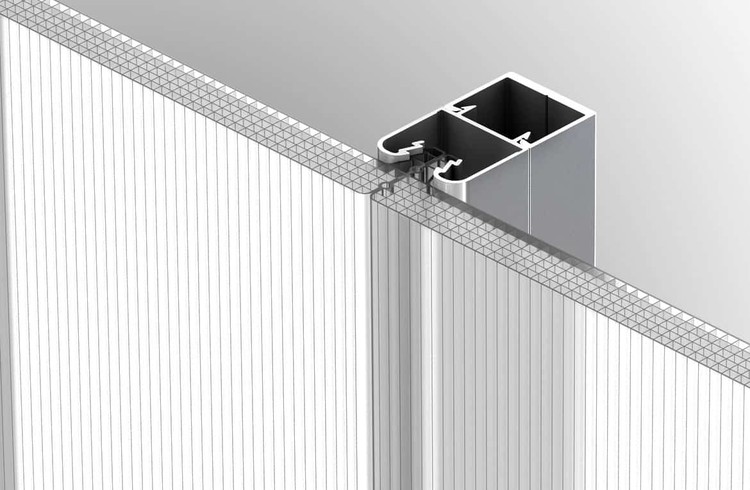
Installing and maintaining polycarbonate cladding panels correctly ensures a long-lasting, aesthetically pleasing, and structurally sound exterior. Proper techniques minimize potential problems and maximize the lifespan of your investment. This section details the steps involved in both installation and ongoing maintenance.
Standard Installation Procedures
Following a step-by-step process is crucial for a successful installation. This ensures the panels are fitted correctly, preventing leaks and damage. Appropriate tools and safety precautions are essential throughout the entire process.
- Preparation: Measure and mark the area where the panels will be installed. Ensure the framing is level, plumb, and structurally sound. Clean the framing surface to remove any dirt, debris, or loose particles.
- Framing: Install the supporting framework, ensuring proper spacing according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. The framing material should be strong enough to support the weight of the panels and withstand environmental stresses.
- Panel Cutting: Carefully measure and cut the polycarbonate panels to the required size using a sharp utility knife or a circular saw with a fine-tooth blade. Wear safety glasses and gloves to prevent injuries.
- Panel Installation: Begin installing panels from the bottom, working your way up. Secure the panels to the framing using appropriate fasteners, such as self-tapping screws or clips. Ensure proper spacing between panels for thermal expansion and contraction.
- Sealants and Flashings: Apply weather-resistant sealant to all joints and seams to prevent water penetration. Install flashing around windows, doors, and other penetrations to further enhance waterproofing.
- Final Inspection: After installation, inspect all panels and connections to ensure a watertight and structurally sound installation. Address any issues immediately.
Common Maintenance Practices, Polycarbonate cladding panels
Regular maintenance extends the life of your polycarbonate cladding. Simple, routine checks and cleaning can prevent costly repairs down the line.
- Regular Cleaning: Clean the panels periodically using mild soap and water. Avoid abrasive cleaners or harsh chemicals that can scratch or damage the surface. A soft sponge or cloth is recommended.
- Inspect for Damage: Regularly inspect the panels for any signs of damage, such as cracks, scratches, or delamination. Address any issues promptly to prevent further damage.
- Check Fasteners: Periodically check all fasteners to ensure they are secure. Tighten any loose screws or replace damaged ones. This prevents panels from becoming loose or dislodged.
- Sealant Inspection: Inspect the sealant around joints and seams for any signs of cracking or deterioration. Reapply sealant as needed to maintain a watertight seal.
Potential Installation and Maintenance Issues and Solutions
Addressing problems quickly is crucial to prevent escalation. Here are some common issues and their solutions:
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Cracked or broken panels | Replace the damaged panels. Ensure proper handling and installation to prevent future damage. |
| Leaks around seams or joints | Inspect and reapply sealant. Ensure proper flashing is installed around penetrations. |
| Loose or damaged fasteners | Tighten or replace loose or damaged fasteners. Ensure the framing is structurally sound. |
| Scratched or dirty panels | Clean the panels with a mild soap and water solution. Avoid abrasive cleaners. |
Environmental Impact and Sustainability: Polycarbonate Cladding Panels

Source: polycipta.com
Polycarbonate cladding, while offering many benefits in terms of durability and aesthetics, has an environmental footprint that needs careful consideration. This section examines the lifecycle impacts of polycarbonate, from manufacturing to disposal, and explores ways to mitigate its environmental effects through sustainable practices and the selection of environmentally friendly alternatives.
The manufacturing process of polycarbonate involves the use of fossil fuels and the release of greenhouse gases. Disposal can also pose challenges, as polycarbonate doesn’t readily biodegrade and can persist in landfills for extended periods. Compared to more sustainable alternatives like sustainably sourced wood or recycled aluminum cladding, polycarbonate generally has a higher embodied carbon footprint. However, its long lifespan and potential for energy savings in building design can partially offset these initial environmental impacts. The overall environmental impact depends heavily on factors like the specific manufacturing process, the panel’s lifespan, and the end-of-life management strategy.
Polycarbonate Recycling and End-of-Life Management
Recycling options for polycarbonate cladding panels are limited compared to some other materials. Many municipalities do not have robust systems for handling polycarbonate waste. However, some specialized recycling facilities exist that can process polycarbonate, often requiring it to be sorted and cleaned beforehand. Initiatives are underway to improve the recyclability of polycarbonate, including research into chemical recycling methods and the development of new materials with improved recyclability. Promoting the use of recycled polycarbonate in new products is also a crucial step towards a more circular economy for this material. Companies and manufacturers are increasingly taking responsibility for the end-of-life management of their products, offering take-back programs or partnering with recycling facilities.
Energy Efficiency Benefits of Polycarbonate Cladding
Polycarbonate’s high light transmission properties contribute significantly to energy efficiency in building design. By allowing ample natural light to penetrate the building, polycarbonate cladding can reduce the reliance on artificial lighting, leading to substantial energy savings. For example, a study conducted by the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory found that using polycarbonate roofing in commercial buildings could reduce lighting energy consumption by up to 30%, depending on the building’s design and climate. Furthermore, the thermal insulation properties of certain polycarbonate panels can minimize heat transfer, reducing the need for heating and cooling. A well-designed building incorporating polycarbonate cladding can achieve significant reductions in both heating and cooling energy consumption, resulting in lower operating costs and a smaller carbon footprint. Consider a hypothetical office building: Replacing traditional glass with high-performance polycarbonate panels could lead to annual energy savings of approximately $10,000 based on a reduction in HVAC and lighting costs, varying based on the building size, climate, and panel specifications. This translates to a reduced carbon footprint and a positive contribution to environmental sustainability.
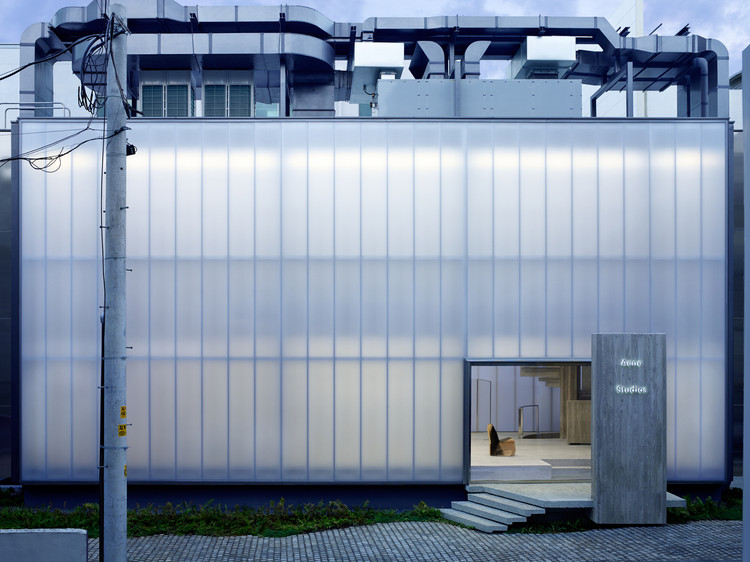
Cost and Economic Considerations
Source: adsttc.com
Choosing the right cladding material involves careful consideration of both upfront and long-term costs. Polycarbonate offers a unique balance, but its overall economic viability depends on several factors. Let’s explore the cost aspects in more detail.
Polycarbonate’s initial cost sits somewhere in the middle range compared to other common cladding materials. While not the cheapest option, its durability and other benefits often offset the higher initial investment over the building’s lifespan.
Comparison of Initial Costs
The initial cost of polycarbonate cladding varies depending on factors like thickness, color, and UV protection. However, a general comparison against other materials provides a useful benchmark. Note that prices are approximate and can fluctuate based on market conditions and the supplier.
| Cladding Material | Approximate Cost per Square Foot | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polycarbonate | $5 – $15 | High impact resistance, light transmission, UV protection options | Higher initial cost than some alternatives |
| Aluminum Composite Panel (ACP) | $3 – $10 | Lightweight, aesthetically pleasing, relatively low maintenance | Less impact resistant than polycarbonate, can dent |
| Metal Cladding (Steel, Aluminum) | $2 – $8 | Durable, long lifespan, various finishes available | Can be susceptible to corrosion, higher maintenance in some climates |
| Vinyl Siding | $1 – $5 | Affordable, easy to install, low maintenance | Less durable than other options, prone to damage from impact |
Long-Term Cost-Effectiveness
While polycarbonate has a higher initial cost, its long-term cost-effectiveness stems from its durability, low maintenance requirements, and potential energy savings. A longer lifespan translates to fewer replacements over time, reducing overall costs.
For instance, a building clad in polycarbonate might require less frequent cleaning and repairs compared to metal cladding prone to corrosion or vinyl siding susceptible to damage. Furthermore, the excellent light transmission properties of polycarbonate can lead to reduced energy consumption for lighting, resulting in significant long-term savings.
Consider a hypothetical scenario: A building with 1000 square feet of cladding. While the initial cost of polycarbonate might be higher, the longer lifespan (20+ years compared to 10-15 years for some alternatives) and reduced maintenance costs over the years can lead to significant cost savings in the long run. This is especially true when factoring in potential energy savings from improved natural light.
Factors Influencing Overall Cost
Several factors contribute to the final cost of polycarbonate cladding. Understanding these factors allows for better budgeting and informed decision-making.
Thickness: Thicker panels are more expensive but offer increased strength and durability. Color: Custom colors and finishes typically add to the cost. Size: Larger panels can reduce installation time and labor costs, potentially offsetting higher material costs. Supplier: Different suppliers offer varying prices and quality levels. It’s crucial to compare quotes from multiple reputable suppliers before making a purchase.
Wrap-Up

Source: uniquepcsheet.com
Polycarbonate cladding panels represent a smart choice for a wide range of projects, balancing durability, aesthetics, and sustainability. By understanding the various types, applications, and installation processes, you can leverage the unique benefits of polycarbonate to create innovative and long-lasting structures. Remember to factor in long-term costs, including maintenance and potential energy savings, to make a truly informed decision. Whether you’re designing a modern office building or a robust industrial facility, polycarbonate offers a compelling solution for enhancing both functionality and visual appeal.





