Galvanized Steel Barricades A Comprehensive Guide
Galvanized steel barricades are more than just barriers; they’re robust, versatile structures crucial for safety and control across diverse industries. From construction sites teeming with activity to bustling event venues and high-security zones, these barricades offer a reliable and durable solution. This guide delves into their material properties, design variations, applications, maintenance, and cost-effectiveness, providing a comprehensive understanding of their importance.
We’ll explore the science behind their corrosion resistance, compare them to other barricade materials, and examine various design features that enhance safety and functionality. We’ll also cover practical aspects like assembly, maintenance, and the overall lifespan of these essential safety components, along with considerations of sustainability and cost.
Galvanized Steel Barricades

Source: made-in-china.com
Galvanized steel barricades are a common sight in construction zones, industrial settings, and even public events. Their robust nature and relatively low cost make them a popular choice for temporary and sometimes permanent barriers. Understanding the material properties of galvanized steel is key to appreciating its effectiveness and longevity.
Galvanized Steel Composition and Durability
Galvanized steel is essentially steel that has been coated with a layer of zinc. The chemical composition of the steel itself varies depending on the grade, but it’s primarily iron (Fe) with additions of carbon (C), manganese (Mn), and sometimes other alloying elements to enhance strength and other properties. The zinc coating is what provides the crucial corrosion resistance. The zinc reacts with the environment preferentially to the iron, protecting the underlying steel from rust even if the zinc coating is scratched or damaged. This sacrificial protection is the primary reason galvanized steel is so durable. A thicker zinc coating generally leads to a longer lifespan and greater corrosion resistance.
Corrosion Resistance in Different Environments
The effectiveness of the galvanization process varies slightly depending on the environment. In coastal areas, where salt spray is prevalent, the zinc coating can degrade more quickly than in drier, less corrosive environments. However, galvanized steel still offers significantly better corrosion resistance than uncoated steel in coastal settings. Similarly, industrial environments with airborne pollutants or chemicals can accelerate corrosion, but galvanized steel remains a more durable option compared to other materials like mild steel. Regular inspections and maintenance, such as repainting damaged areas, can further extend the life of galvanized steel barricades in harsh environments.
Strength and Weight Comparison
Galvanized steel barricades offer a good balance of strength and weight. Compared to aluminum barricades, galvanized steel is significantly stronger and more resistant to impacts, but it is also heavier. Concrete barricades, while extremely strong and heavy, are less portable and more difficult to install and relocate. The choice of material often depends on the specific application; for instance, a high-traffic area might necessitate the robust strength of galvanized steel or concrete, while a temporary, easily movable barricade might benefit from the lighter weight of aluminum.
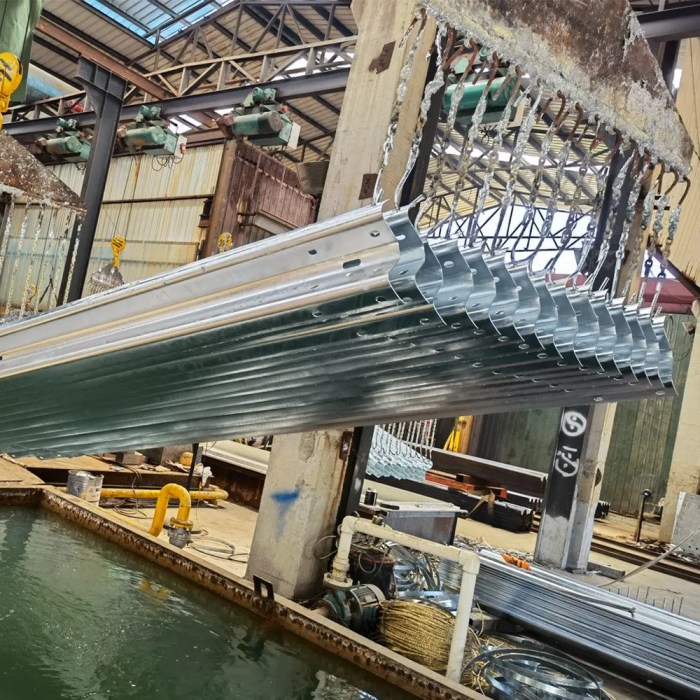
Manufacturing Process of Galvanized Steel Barricades
The manufacturing process involves several key steps, from the initial steel production to the final assembly of the barricade.
| Process Step | Description | Materials Used | Quality Control Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel Sheet Production | Steel is melted and cast into large slabs, then rolled into sheets of the desired thickness. | Iron ore, scrap steel, alloying elements | Chemical composition analysis, thickness measurement |
| Galvanizing | Steel sheets are passed through a molten zinc bath, creating a protective zinc coating. | Zinc, steel sheets | Coating thickness measurement, visual inspection for defects |
| Forming | Steel sheets are shaped into the desired barricade profile using presses or rollers. | Galvanized steel sheets | Dimensional accuracy checks, surface finish inspection |
| Welding | Individual sections are welded together to create the complete barricade structure. | Galvanized steel sections, welding consumables | Weld integrity testing (e.g., visual inspection, radiography), strength testing |
Design and Functionality of Galvanized Steel Barricades
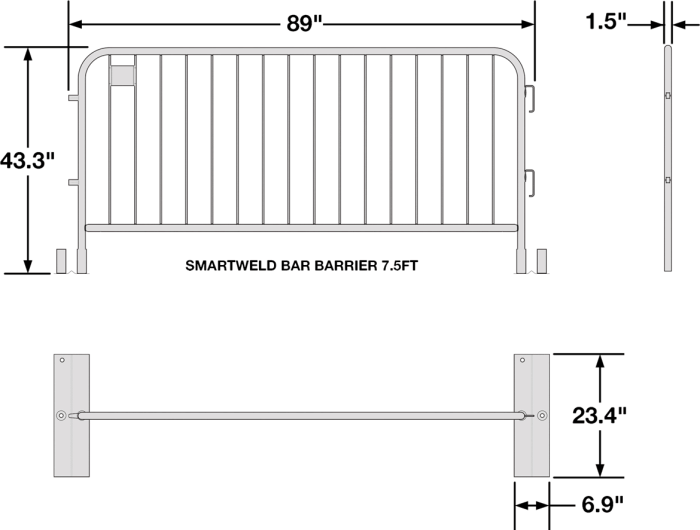
Source: startsafety.com
Galvanized steel barricades offer a robust and versatile solution for a wide range of applications, from construction sites to crowd control events. Their design and functionality are key to their effectiveness and longevity. Understanding the different types, their strengths, and assembly is crucial for choosing the right barricade for a specific need.
Design Variations of Galvanized Steel Barricades
Galvanized steel barricades come in several designs, each tailored to specific needs and environments. Temporary barricades are lightweight and easily moved, perfect for short-term use. Permanent barricades are heavier and more durable, designed for long-term installations. Retractable barricades offer a flexible solution, allowing for easy storage and deployment as needed. Let’s explore the features and applications of each.
Temporary barricades are typically lightweight and constructed from thinner-gauge steel. They often feature simple, interlocking designs for easy assembly and disassembly. Their applications include short-term traffic control, crowd management at events, and temporary site demarcation during construction. They are designed for portability and ease of handling, making them ideal for frequent relocation.
Permanent barricades are much heavier and more robust, typically constructed from thicker gauge steel. They often feature a more substantial base for increased stability and are designed to withstand significant impact and harsh weather conditions. Their applications include long-term traffic control, security barriers, and permanent site boundaries. They are designed for longevity and resistance to damage.
Retractable barricades are a hybrid of the two. They are typically comprised of a sturdy base and a retractable section that can be easily extended or retracted. This allows for flexible deployment and compact storage when not in use. Their applications are diverse, ranging from temporary crowd control to flexible security barriers in various settings.
Load-Bearing Capacity and Stability
The load-bearing capacity and stability of galvanized steel barricades vary greatly depending on the design and materials used. Thicker gauge steel and reinforced designs provide higher load-bearing capacity and better stability against impact and wind forces. For example, a temporary barricade might withstand a moderate impact, while a permanent barricade designed for high-traffic areas might be engineered to resist much stronger forces. The base design also significantly impacts stability. Wider bases and added weights offer greater resistance to tipping or displacement, especially in windy conditions. Consideration should be given to the specific environmental conditions and expected loads when selecting a barricade. Proper installation is also critical for optimal stability.
Ease of Assembly and Disassembly
The ease of assembly and disassembly varies greatly between different barricade types. Temporary barricades are generally designed for quick and easy assembly, often involving simple interlocking mechanisms or bolt-on connections. Permanent barricades, due to their robust construction, may require more time and effort for assembly, sometimes involving welding or more complex fastening systems. Retractable barricades usually involve a simple mechanism for extending and retracting the barrier, offering a balance between convenience and durability.
Here are the steps involved in assembling a common type of temporary galvanized steel barricade:
- Unpack the barricade components and ensure all parts are present.
- Align the base sections and connect them using the provided interlocking mechanisms.
- Attach the upright sections to the base, ensuring secure connections.
- If applicable, attach any reflective markings or additional safety features.
- Check the stability of the assembled barricade before deploying it.
Safety Features
Safety is paramount in barricade design. Many incorporate reflective markings for enhanced visibility, especially in low-light conditions. Handles are often included to facilitate easy and safe movement and deployment. Interlocking mechanisms ensure secure connections between components, preventing accidental separation or collapse. Some barricades may also include features such as weighted bases for increased stability or additional bracing for enhanced strength. The specific safety features incorporated will depend on the intended application and the level of risk involved. For instance, barricades used in high-traffic areas or hazardous environments may have more robust safety features than those used in less demanding settings.
Applications and Uses of Galvanized Steel Barricades

Source: vivablast.com
Galvanized steel barricades are incredibly versatile, finding applications across a wide range of industries due to their robust nature and resistance to corrosion. Their strength and durability make them ideal for situations demanding high levels of safety and longevity, even in challenging environments. This section will explore specific uses and the reasons behind their selection in various contexts.
The primary benefit of using galvanized steel barricades lies in their combination of strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. This makes them a cost-effective long-term solution compared to alternatives that may require more frequent replacement due to weathering or damage.
Construction Site Applications
Galvanized steel barricades are indispensable on construction sites for controlling pedestrian and vehicle traffic, delineating hazardous areas, and ensuring worker safety. Their heavy-duty construction withstands impacts from heavy machinery and accidental collisions. The galvanized coating protects against rust and degradation, extending their lifespan even in harsh outdoor conditions, exposed to rain, sun, and construction debris. For example, a large-scale highway project might utilize hundreds of these barricades to create safe walkways for workers and to separate active construction zones from public areas.
Event and Crowd Control
At large-scale events, such as concerts, festivals, and sporting events, galvanized steel barricades are crucial for crowd management and safety. Their ability to withstand significant pressure from large crowds makes them a safer alternative to lighter materials. The galvanized coating ensures they remain structurally sound even in wet conditions, preventing accidents from slippery surfaces. Imagine a music festival; strategically placed barricades guide pedestrian flow, prevent overcrowding near stages, and provide a safe barrier between performers and the audience.
Security and Perimeter Protection
Galvanized steel barricades are often employed for security purposes, creating temporary or permanent barriers around sensitive areas. Their robust construction and resistance to tampering make them suitable for protecting construction sites, government buildings, or private properties. The high visibility of the galvanized steel also acts as a deterrent. For instance, a construction site securing expensive equipment might use galvanized steel barricades to create a secure perimeter, preventing unauthorized access and theft.
Case Study: Hurricane Protection, Galvanized steel barricades
During Hurricane Katrina, many areas used galvanized steel barricades to protect critical infrastructure and residential areas from flooding. Their strength allowed them to withstand the strong winds and storm surges, proving their effectiveness in extreme weather conditions. The galvanized coating prevented rapid rusting and deterioration after exposure to saltwater, ensuring their continued functionality even after the storm had passed.
Comparative Table of Galvanized Steel Barricade Applications
| Industry | Specific Application | Barricade Type | Environmental Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Traffic control, hazard delineation | Heavy-duty, high-visibility | Exposure to rain, sun, and construction debris |
| Events | Crowd control, pedestrian guidance | Modular, easily deployable | Potential for wet conditions, large crowds |
| Security | Perimeter protection, access control | High-strength, tamper-resistant | Exposure to elements, potential vandalism |
| Emergency Management | Flood barriers, disaster response | Heavy-duty, stackable | Extreme weather conditions, potential flooding |
Maintenance and Lifespan of Galvanized Steel Barricades

Source: alicdn.com
Proper maintenance significantly extends the lifespan of galvanized steel barricades, protecting your investment and ensuring continued safety and functionality. Neglecting maintenance can lead to premature deterioration and costly repairs or replacements. Understanding the factors that affect their longevity and implementing a regular maintenance schedule is crucial.
Environmental Impact on Galvanized Steel
Exposure to various environmental factors accelerates the degradation of galvanized steel. Salt spray from coastal environments is particularly damaging, causing rapid corrosion through a process called galvanic corrosion. This occurs when the zinc coating reacts with the salt, leading to the formation of zinc chloride, which is then washed away, exposing the underlying steel to further corrosion. Similarly, exposure to acidic chemicals, such as those found in industrial areas or from spilled materials, can also significantly reduce the lifespan of the barricades. Industrial pollutants containing sulfur dioxide can also accelerate corrosion. The severity of the damage depends on the concentration and duration of exposure to these elements. For example, barricades placed near a busy highway with heavy salt use in winter will degrade much faster than those in a dry, sheltered location.
Signs of Deterioration and Repair Methods
Recognizing the signs of deterioration is vital for timely intervention. Rust is the most obvious indicator of corrosion, typically appearing as orange or brown patches on the steel surface. Blistering or flaking of the zinc coating is another sign that the protective layer is failing. Significant dents, bends, or cracks compromise the structural integrity of the barricades and need immediate attention. Repair methods depend on the severity of the damage. Minor surface rust can often be addressed with wire brushing and repainting with a zinc-rich primer and a suitable topcoat. More extensive damage may require section replacement or even complete barricade replacement. Welding repairs should only be undertaken by qualified professionals to ensure structural integrity and safety.
Cleaning and Inspection Procedures
Regular cleaning and inspection are essential for maintaining the condition of your galvanized steel barricades. A proactive approach helps prevent small problems from escalating into costly repairs.
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect all surfaces of the barricade for signs of rust, dents, cracks, or loose components. Pay close attention to areas prone to damage, such as corners and edges.
- Cleaning: Use a stiff brush or pressure washer to remove dirt, debris, and loose rust. Avoid abrasive cleaners that could damage the zinc coating. For stubborn stains, consider using a mild detergent solution.
- Rust Treatment: If rust is present, remove it using a wire brush or sandpaper. Apply a zinc-rich primer to the affected area before repainting with a durable topcoat.
- Tightening of Fasteners: Check and tighten any loose bolts or screws to ensure the barricade remains structurally sound.
- Documentation: Maintain a record of inspection dates, findings, and any repairs performed. This helps track the condition of the barricades over time and facilitates proactive maintenance planning.
Cost and Sustainability Considerations: Galvanized Steel Barricades
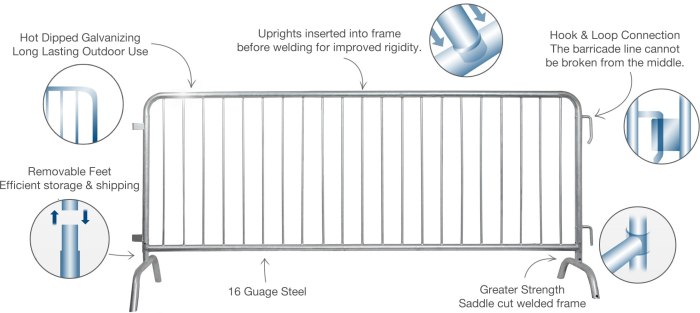
Source: startsafety.com
Galvanized steel barricades offer a compelling blend of durability and longevity, but their overall cost-effectiveness and environmental impact are crucial factors to consider. This section will compare galvanized steel to alternative barricade materials, analyze its lifecycle environmental footprint, and highlight its recyclability within the context of sustainable construction.
Cost Comparison of Barricade Materials
Choosing the right barricade material often involves a careful balancing act between upfront costs, maintenance needs, and the material’s lifespan. While galvanized steel might have a higher initial investment compared to some alternatives, its durability translates to lower long-term maintenance expenses and a significantly extended service life. This table provides a comparative overview, though actual costs can vary based on factors such as quantity purchased, supplier, and geographical location.
| Material | Initial Cost | Maintenance Cost (per year) | Lifespan (years) | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Galvanized Steel | High | Low | 20-30+ | Moderate (due to manufacturing and zinc coating, but highly recyclable) |
| Plastic (HDPE) | Medium | Medium | 5-10 | Moderate (production uses fossil fuels; recyclability varies) |
| Wood | Low | High | 3-5 | Low to Moderate (depending on sourcing and treatment; disposal can be problematic) |
| Concrete | Medium to High | Low | 20+ | High (cement production is carbon-intensive; not easily recyclable) |
Environmental Impact of Galvanized Steel Barricades
The manufacturing process of galvanized steel involves energy consumption for steel production and the application of the zinc coating. This contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion. However, the substantial lifespan of galvanized steel barricades mitigates some of this impact. Compared to frequently replaced alternatives like wood or plastic, the overall environmental burden over the barricade’s lifetime might be lower. Furthermore, the zinc coating itself protects the steel from corrosion, extending its lifespan and reducing the need for replacements. For example, a study by the World Steel Association shows that steel production is continuously improving its environmental performance through technological advancements and improved recycling rates.
Recyclability and Sustainable Construction
Galvanized steel is highly recyclable. At the end of its service life, the steel can be melted down and reused in new steel products, significantly reducing the demand for virgin materials. This closed-loop system minimizes waste and conserves natural resources. Incorporating recycled galvanized steel into new barricades further reduces the environmental footprint. Many construction companies are increasingly prioritizing sustainable materials and practices, and the recyclability of galvanized steel aligns perfectly with this trend, contributing to a more circular economy within the construction industry. The use of recycled steel also reduces the overall energy required for steel production, further enhancing its environmental benefits.
Conclusion

Source: nottinghamzincgroup.com
Galvanized steel barricades represent a smart investment in safety and security across various sectors. Their durability, versatility, and relatively low maintenance requirements make them a cost-effective choice for long-term use. Understanding their design, applications, and maintenance is key to maximizing their lifespan and ensuring they effectively serve their intended purpose. By carefully considering factors like environmental conditions and anticipated usage, you can select the optimal galvanized steel barricade solution for your specific needs.





