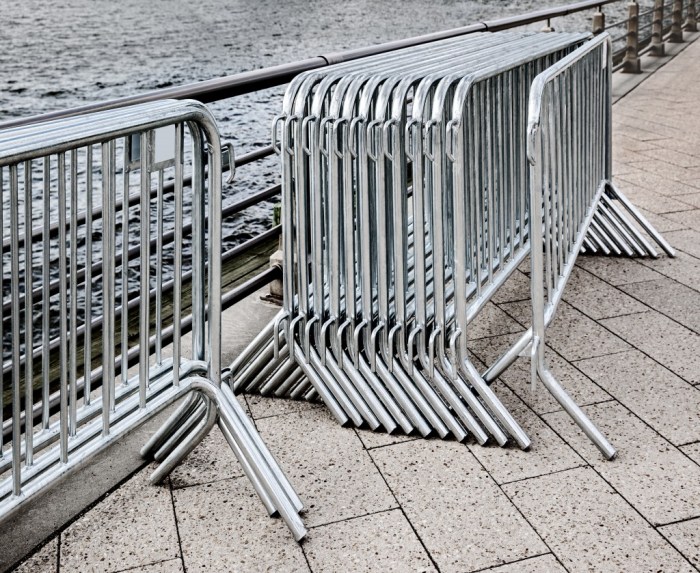
Interlocking Barricades A Comprehensive Guide
Interlocking barricades are far more than just barriers; they’re versatile tools for safety and security across various sectors. From managing traffic flow at bustling construction sites to securing high-profile public events and even bolstering military operations, these robust systems play a vital role. This guide delves into the different types, applications, installation, maintenance, and cost-effectiveness of interlocking barricades, providing a complete overview for anyone needing to understand their functionality and impact.
We’ll explore the diverse designs, materials (like plastic, metal, and concrete), and strengths and weaknesses of each type. We’ll also look at they’d current situations, the step-by-step installation process, maintenance needs, and the overall environmental and economic implications. Get ready to become an expert on interlocking barricades!
Types of Interlocking Barricades

Interlocking barricades offer a versatile and adaptable solution for crowd control, security, and traffic management. Their design allows for quick deployment and easy storage, making them a popular choice across various sectors. Understanding the different types available, their strengths and weaknesses, is crucial for selecting the most appropriate barricade for a specific need.
Several factors influence the choice of interlocking barricade, including the level of security required, the anticipated duration of deployment, and the budget. Material, design, and ease of handling all contribute to the overall effectiveness and practicality of the chosen system.
Interlocking Barricade Designs and Materials
Various interlocking barricade designs utilize different materials, each offering a unique combination of strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Common materials include plastic, metal, and concrete, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
| Type | Material | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic Interlocking Barricades | High-density polyethylene (HDPE) or similar plastics | Lightweight, easy to handle and transport, relatively inexpensive, brightly colored for high visibility, reusable. | Less durable than metal or concrete, susceptible to damage from impact or extreme weather conditions, may not provide sufficient security in high-risk situations. |
| Metal Interlocking Barricades | Steel, aluminum, or other metals | Strong and durable, resistant to damage, provides a higher level of security than plastic barricades, and can be designed for heavy-duty applications. | Heavier and more difficult to handle than plastic barricades, more expensive, can rust or corrode over time (especially steel), and may require more storage space. |
| Concrete Interlocking Barricades | Reinforced concrete | Extremely durable and resistant to damage, it provides the highest level of security, suitable for long-term or permanent installations. | Very heavy and difficult to move, expensive, requires specialized equipment for handling and installation, less versatile than plastic or metal barricades. |
Applications of Interlocking Barricades

Interlocking barricades, with their robust design and ease of assembly, find widespread use in a variety of settings where safety and security are paramount. Their adaptability allows them to be configured for diverse needs, from controlling pedestrian flow at a concert to securing a construction site. The modular nature of these barricades ensures efficient deployment and easy storage, making them a cost-effective solution for temporary and long-term applications.
Interlocking barricades are used to create barriers that protect people and property from hazards. The strength of the interlocking system prevents easy displacement, providing a substantial level of security, even under duress. Their versatility allows for creating various barrier configurations depending on the specific needs of the situation.
Construction Site Safety
Interlocking barricades are essential for maintaining safety on construction sites. They effectively delineate work zones from public areas, preventing accidental entry by unauthorized personnel. This minimizes the risk of injuries from falling debris, heavy machinery, or ongoing construction activities. They also help organize the site, separating different work areas and directing pedestrian and vehicle traffic.
- Advantages: Easy to assemble and reconfigure as needed; robust enough to withstand impacts; clearly define hazardous areas; improve site organization; contribute to a safer work environment.
- Disadvantages: Can be expensive initially; may require additional measures (like signage) for maximum effectiveness; can be cumbersome to move in large quantities; may not be suitable for all terrains (e.g., very uneven ground).
Public Event Security
At large public gatherings like concerts, festivals, or sporting events, interlocking barricades are crucial for crowd control and managing pedestrian flow. They create safe pathways, prevent overcrowding in designated areas, and channel movement towards exits in case of emergencies. They can also be used to create secure VIP areas or backstage access points.
- Advantages: Quickly deployable to manage large crowds; help prevent bottlenecks and stampedes; provide a clear visual barrier; enhance security by controlling access; are relatively easy to transport and store.
- Disadvantages: May not be sufficient to stop determined individuals; require careful planning and placement to be effective; can create visual obstructions; need regular maintenance to ensure they remain sturdy.
Military Operations, Interlocking barricades
In military settings, interlocking barricades can be used to establish perimeter security, create checkpoints, or fortify defensive positions. Their strength and ability to withstand impacts make them useful in temporary fortifications or for creating barriers against vehicle attacks. They can also be used to control access to sensitive areas or protect personnel.
- Advantages: Quickly erected temporary defenses; offer a degree of protection against small arms fire and vehicle impacts; easily transportable; can be adapted to various terrain types; provide clear demarcation of controlled areas.
- Disadvantages: Offer limited protection against heavier weaponry; can be breached with sufficient force; require regular inspection and maintenance in harsh conditions; may not be sufficient on their own for comprehensive security.
Traffic Control
Interlocking barricades are used in various traffic control scenarios, such as road closures due to accidents, construction, or special events. They effectively redirect traffic flow, ensuring the safety of workers and the public. Their bright colors and reflective properties increase visibility, even at night.
- Advantages: Easily deployed to reroute traffic; clearly visible, even in low-light conditions; robust enough to withstand impacts from vehicles; relatively inexpensive compared to other traffic control measures; can be easily removed once the need is over.
- Disadvantages: May require additional signage for optimal effectiveness; can be damaged by reckless driving; may not be suitable for high-speed traffic areas; requires proper placement and maintenance to prevent accidents.
Installation and Deployment of Interlocking Barricades
Installing and deploying interlocking barricades effectively requires careful planning and execution to ensure both safety and effectiveness. The process varies slightly depending on the specific barricade type and the site conditions, but the general principles remain consistent. Proper installation is crucial for maximizing the barricades’ performance and preventing accidents.
- Site Preparation and Planning: Before beginning installation, thoroughly assess the area. Clear the installation zone of any debris, obstructions, or hazards that could interfere with the process or create safety risks. Measure the area to determine the exact number of barricades needed and plan their layout. Consider traffic flow and pedestrian access when determining placement. For example, if installing barricades around a construction site, ensure adequate space for emergency vehicle access.
- Gathering Necessary Tools and Equipment: Depending on the type of interlocking barricade, you may need various tools. Common tools include gloves, safety glasses, possibly a measuring tape, and potentially a level for precise placement. Some heavier barricades may require additional tools for anchoring or securing to the ground, such as shovels, post-hole diggers, or specialized anchoring kits. Always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for specific tool requirements.
- Connecting the Barricades: Carefully connect the individual barricade sections according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Most interlocking systems are designed for simple, straightforward connection. Ensure each connection is secure and properly aligned to prevent gaps or weak points. Pay close attention to any locking mechanisms or fasteners. Incorrect connections can compromise the overall stability and effectiveness of the barricade line.
- Securing the Barricades: Once the barricade line is assembled, secure it to prevent movement or tampering. Methods of securing vary depending on the barricade type and location. This might involve anchoring to the ground using stakes, weights, or filling the base with sand or water. In high-traffic areas or locations prone to strong winds, additional securing measures might be necessary to maintain stability. For instance, heavy-duty concrete blocks can provide additional weight and stability to prevent the barricades from being easily moved.
- Final Inspection and Adjustments: After installation, conduct a thorough inspection of the entire barricade line. Check for any loose connections, gaps, or misalignments. Make any necessary adjustments to ensure the barricades are stable, secure, and properly positioned. Ensure the barricades are visible, particularly in low-light conditions. Consider using reflective tape or other markings to enhance visibility.
Safety Precautions During Installation and Deployment
Safety is paramount during the installation and deployment of interlocking barricades. Several precautions should be followed to minimize the risk of accidents or injuries.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE, including safety glasses, gloves, and sturdy footwear. Depending on the specific situation, additional PPE such as high-visibility vests may also be necessary.
- Traffic Control: If installing barricades in an area with traffic, implement appropriate traffic control measures to ensure the safety of workers and the public. This could involve using traffic cones, warning signs, or flaggers to divert or control traffic flow.
- Lifting and Handling: Use proper lifting techniques to avoid strain or injury when handling barricades, especially heavier models. If assistance is needed, get help from a colleague to prevent accidents.
- Environmental Considerations: Be aware of environmental conditions, such as uneven ground, inclement weather, or extreme temperatures. Adjust installation methods as needed to ensure stability and safety in challenging conditions. For example, avoid installation during periods of heavy rain or high winds.
- Post-Installation Monitoring: Regularly inspect the installed barricades for damage or displacement. Make necessary repairs or adjustments promptly to maintain their effectiveness and ensure continued safety.
Maintenance and Durability of Interlocking Barricades

Interlocking barricades, while robust, require regular maintenance to ensure their continued effectiveness and longevity. Neglecting maintenance can lead to reduced safety, increased repair costs, and ultimately, the need for premature replacement. Understanding common issues and implementing proper maintenance practices are crucial for maximizing the lifespan of these vital safety components.
Proper maintenance extends the useful life of interlocking barricades, preventing costly repairs and ensuring continued effectiveness in protecting personnel and property. Regular inspections, prompt repairs, and appropriate storage contribute to the overall durability and safety of these systems. Ignoring maintenance can lead to compromised structural integrity, posing safety risks and potentially causing significant damage in the event of an accident or emergency.
Common Problems and Their Causes
Several factors contribute to the deterioration of interlocking barricades. These include environmental exposure, improper handling, and insufficient maintenance. Understanding these causes allows for the implementation of targeted preventative measures.
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Cracked or broken sections | Impact damage, exposure to extreme temperatures, and material fatigue | Replace damaged sections. Consider using reinforced or UV-resistant materials for future installations in harsh environments. |
| Loose or dislodged connectors | Improper installation, wear and tear, impact damage | Tighten or replace loose connectors. Ensure proper installation techniques are followed during setup and takedown. |
| Fading or discoloration | Exposure to UV radiation, weathering | Regular cleaning can help maintain the appearance. Consider using UV-resistant materials for installations in areas with prolonged sun exposure. |
| Rust or corrosion | Exposure to moisture, salt spray (coastal areas) | Regular cleaning and application of rust inhibitors or protective coatings. Choose materials with corrosion-resistant properties for installations in susceptible environments. |
| Deformation or bending | Heavy loads, impact, improper handling | Replace damaged sections. Ensure proper handling procedures are followed during transport and installation. Avoid overloading the barricades. |
Recommended Maintenance Procedures
A comprehensive maintenance program should include regular inspections, cleaning, and repairs. These procedures ensure that the barricades remain structurally sound and effective in fulfilling their intended purpose.
A visual inspection should be performed at least once a month, or more frequently in high-use areas or harsh environments. This inspection should check for any signs of damage, loose connectors, or corrosion. Regular cleaning, using appropriate cleaning agents, helps remove dirt and debris that can accelerate wear and tear. Prompt repairs are essential to prevent minor issues from escalating into major problems. Proper storage, when not in use, protects the barricades from damage and environmental degradation.
Cost-Effectiveness and Environmental Impact
Choosing the right interlocking barricade involves careful consideration of both cost and environmental impact. Different materials offer varying levels of initial investment, ongoing maintenance needs, and long-term environmental consequences. Understanding these factors is crucial for making an informed decision that balances budget constraints with sustainability goals.
The total cost of ownership for interlocking barricades extends beyond the initial purchase price. Factors like durability, maintenance requirements (such as cleaning or repair), and lifespan significantly influence the overall cost-effectiveness. Similarly, the environmental footprint encompasses the raw materials used in manufacturing, the energy consumed during production and transportation, and the eventual disposal or recycling options at the end of the barricade’s life. Let’s delve into a comparative analysis.
Comparative Analysis of Interlocking Barricade Costs and Environmental Impact
The following table summarizes the cost and environmental impact of various common interlocking barricade materials. Note that these are estimates and can vary based on specific product features, supplier, and location. Maintenance costs are also highly dependent on usage and environmental conditions.
| Material | Initial Cost | Maintenance Cost | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic (Recycled HDPE) | Moderate | Low | Relatively low; recyclable, but production requires energy. The use of recycled materials significantly reduces the impact. |
| Steel | High | Moderate (rust prevention, potential damage repair) | Moderate to High; steel production is energy-intensive and contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. Recycling is possible, but it requires energy. |
| Concrete | High | Low (generally very durable) | Moderate; concrete production has a significant carbon footprint due to cement manufacturing. Disposal can be challenging. |
| Rubber (Recycled Tires) | Moderate to High | Low | Relatively low; utilizes recycled materials, reducing landfill waste. However, the manufacturing process still requires energy. |
Illustrative Examples of Interlocking Barricades in Use

Interlocking barricades offer versatile solutions for a wide range of security and crowd control needs. Their adaptability means they can be deployed effectively in diverse environments, achieving specific goals efficiently. Let’s look at three real-world examples to illustrate their practical applications.
Construction Site Security
This example showcases the use of interlocking plastic barricades at a large-scale construction site in a bustling city center. The site, bordered by a busy street and pedestrian walkways, required robust security measures to protect workers and the public. Hundreds of bright orange and white plastic barricades, each approximately three feet high and four feet wide, were interconnected to form a continuous, easily configurable barrier around the entire perimeter. The bright colors provided high visibility, while the interlocking design ensured stability even against accidental impacts from vehicles or pedestrians. The ease of assembly and disassembly allowed for efficient adjustments as the construction progressed, and the durable plastic construction withstood the wear and tear of a busy urban environment. The result was a safe and clearly defined work zone that minimized risks for both workers and the public. The modular nature allowed for quick reconfiguration of access points as needed.
Emergency Response at a Public Event
A large music festival in a park setting required a quick and efficient method for crowd control and emergency response. Thousands of attendees required well-defined pathways and safe zones. Metal interlocking barricades, painted a muted gray to blend somewhat with the surroundings but still visible, were deployed to create designated entry and exit points, separate areas for VIP access, and pathways directing foot traffic. These barricades were significantly taller and heavier than the plastic ones used at the construction site, around five feet high and six feet wide, reflecting the higher security needs of a large crowd. Their strength prevented accidental breaching and provided a sense of security for attendees. In the event of an emergency, these barricades were quickly reconfigured to create safe escape routes and designated assembly areas. The strength and stability of the metal barricades proved invaluable in managing the flow of a large, potentially chaotic crowd.
Temporary Road Closure During a Marathon
A city marathon required the temporary closure of several roads for the safety of runners and spectators. Lightweight, yet sturdy, interlocking plastic barricades in bright neon yellow and black were used to cordon off the race route. These barricades, approximately two and a half feet high and three feet wide, were quickly deployed by volunteers along the route. Their lightweight nature made them easy to handle and maneuver, allowing for efficient setup and takedown. The bright colors provided excellent visibility, warning drivers and pedestrians of the road closure. The interconnected design prevented unauthorized access to the race route, ensuring the safety of the runners. After the marathon, the barricades were easily removed and stored for future use, minimizing city traffic flow disruption. The ease of deployment and removal, combined with the visual impact of the bright colors, ensured a safe and well-managed event.
Last Point

Interlocking barricades represent a crucial element in maintaining safety and order across a wide range of environments. Understanding their diverse applications, proper installation, and ongoing maintenance is key to maximizing their effectiveness and ensuring long-term value. By carefully considering the factors outlined in this guide – from material selection and cost analysis to environmental impact and safety protocols – you can confidently select and deploy the ideal interlocking barricade system for your specific needs. Remember, safety first!